The difficulties of cast iron metallographic preparation
The main challenge is to keep graphite cast iron sample preparation of the original shape and size, to ensure that the correct characterization of microstructure of cast iron.

Figure 4: contains the flake graphite gray cast iron, inadequate polishing (200 x magnification:)
Figure 5: contains the flake graphite gray cast iron, polishing display correct (200 x magnification:)
Under a microscope, the graphite's image seems to be two-dimensional.But it is three-dimensional.This means that in the process of grinding and polishing, a certain proportion of graphite was cut very shallow, only very weak fixation in the matrix.Therefore, graphite will may not be fully retained, especially very large graphite or accumulate graphite pieces.As a result, the graphite phase are not always well retained or polishing.
In malleable cast iron, the graphite exists in the form of flocculent mass or tempering carbon.This is a kind of fragile graphite, it is difficult to retain in metallographic preparation process.
The preparation of common error is insufficient to eliminate the blur matrix metal after grinding, make the real shape and size of graphite is only a blur.This special in the ferritic and austenitic cast iron, they are easy to deformation and scratches.For these materials, a thorough diamond grinding and the final polishing is very important.
Most of the cast iron standard microscope with magnification of 100 times, this makes the graphite looks black.Carbon to verify whether completely retained, however, requires a higher magnification, because good polishing of graphite is grey.
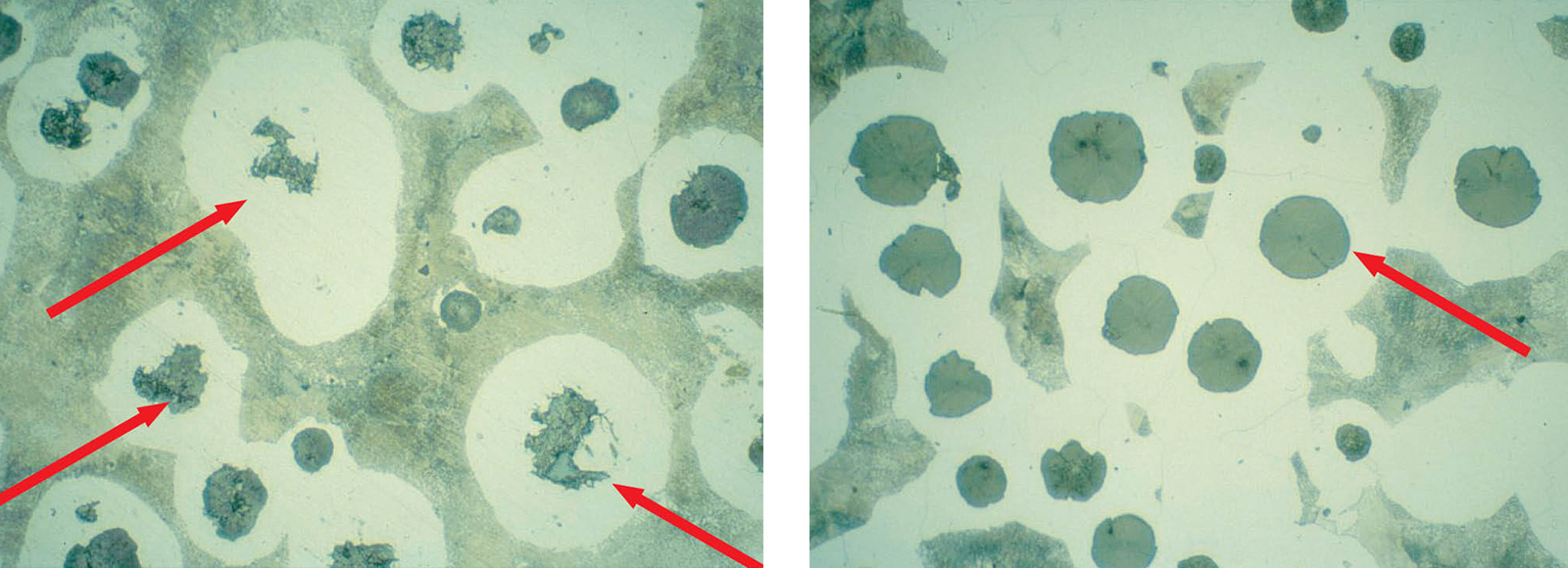
Figure 6: inadequate polishing graphite particle covered with metal stains, etching with nitric acid 3% ethanol (200 x magnification:)
Figure 7: polishing, right shows the shape and size of graphite for evaluating, using 3% ethanol nitrate etching (200 x magnification:)

Figure 8: polishing good flake graphite (500 x magnification:)










